OUR PHILOSOPHY OF THE PAGE
EXPLANATION OF THE VARIABLES AND THE USE OF THE SEARCH ENGINE
USE OF THE SEARCH ENGINE
The use of this page is pretty straightforward: in the upper-left window you select the index according to which you want to browse the plants and which is then loaded into lower-left window. Selecting a plant in that window loads then the record for that plant in the right window.
EXPLANATION OF INDIVIDUAL RECORDS
These records contain information about individual plants. As of now, mostly visual information and codes are presented. In the future, we plan to expand the descriptive section (which is given for a few plants; a good example of the text can be seen for instance here: Rhodophiala rhodolirion (Añañuca de cordillera). The primary objective of our records is to help identify the plant. In this sense the records act as on-line herbarium of live plants. We include many photos of the plant, both artistic, trying to bring out the individuality and beauty of the plant, of its habitat or of the plant in its habitat, and descriptive, which show all of the details of the plant, like leaves, stalks, induments, fruits, flowers, internal parts of the flower; some of these images now include a scale and many are close-up photographs.
We are strongly convinced that the most urgent task on hand is to expand the number of species presented, because there is a notorious lack of literature, especially with clear and detailed images of plants, so that our page would become a guide to easily identify and confirm the doubtful identification of Chilean plants.
As a next step we would then expand the descriptive parts so as to convert the herbarium into an Interactive Encyclopedia of Chilean Flora.
EXPLANATION OF ICONS
USES
Here are the symbols which describe the uses of the plant:
| Medicinal | |
| Edible | |
| POISONOUS | |
| Weed | |
| Timber plant, including carbon and firewood uses, | |
| "Industrial", that is, the products of the plant were used in industrial processes or as a replacement of the industrial products. Examples: Coloring substances, rat poisons, tanning, etc. | |
| Fodder (for domestic animals) | |
| Ornamental | |
| No Data |
FREQUENCY
Our current definition of frequency is the probability of finding the plant in an environment defined by the region (latitude range), elevation, light exposure, and humidity. In this sense, some plants which in the literature are commonly defined as "rare," or "very rare" are considered to be "frequent" or "not very frequent". This is the case for instance for Alstroemeria pseudospathulata.
This is also a compound variable and in the future we would prefer to use two variables instead: "frequency of presence" and "frequency within the area of presence". The "frequency of presence" would refer to the percentage of areas which contain the plant, out of the total areas which correspond to the potential habitat of the plant as defined by environmental factors. "Frequency within the area of presence" (or scattering) would refer to the probability of finding that plant in the area of plant presence.
| Very frequent | The plant represents an important and dominant part of the vegetation. It is almost certain to be seen in its potential habitat. |
| Frequent | The plant can be frequently found in most of its potential habitats and its presence is quite prominent where it is present. |
| Not frequent | The plant is scattered and in many potential habitats it is not to be found. |
| Rare | Very small population groups occupy a very small percentage of the potential habitats. |
| Extremely rare | Isolated, scattered individuals or extremely small population groups which are unique. Extremely unlikely to be seen without concrete location information. |
ORIGIN
| Foreign | This is a plant which was introduced and now escaped from cultivation and is growing in wild conditions. |
| Native | This is a plant which had its habitat in Chile, but which also grows in wild conditions in other countries. |
| Endemic | This is a plant which grows in wild conditions only in Chile. |
DISTRIBUTION
 | The green color of the region indicates the presence of the plant in that region. |
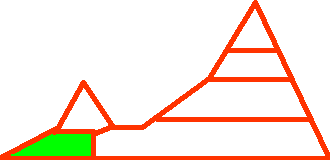
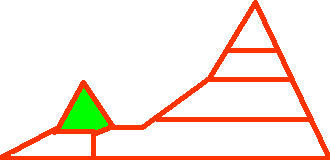
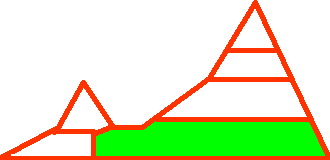
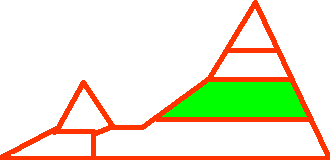
ALTITUDE
The altitude is given in relative terms and this variable also includes the relative location to the coast, i.e. whether the plant grows in vicinity of the coast or not.
| Symbol | Meaning |
 | Coastal areas of up to 500 m |
 | Coastal mountains 500 - 2000 m. (It refers to the coastal range of mountains which run along the most part of coastal Chile, with the exception of extreme South (11th and 12th Region). For the 11th and 12th region this symbol is equivalent to "Interior valleys" and "Medium elevation" |
 | Interior valleys (100 m - to the limit of the occasional snowfall |
 | Medium elevation. For the central and southern zone (Region Metropolitana and 6th through 12th Region) it is defined as an area from where occasional snowfall can be expected for short periods (not necessarily all years) up to the timber line limit. For more northern regions it is a fixed altitude range: 2000-3000 m. |
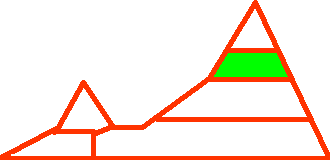 | High elevation. Areas adjacent to the timber line. In the north, areas with an altitude of 3000 - 4000 m. |
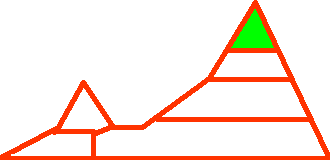 | Extreme elevation. Areas adjacent to the limit of vegetation. |
| Altitude | Tal-tal | La Serena | Santiago | Talca | Temuco | P. Montt | Punta Arenas |
 | 4000-5000 | 3500-4500 | 3000-4000 | 2600-3500 | 2000-3000 | 1500-2200 | 1000-1500 |
 | 3000-4000 | 2600-4000 | 2200-3500 | 2000-2600 | 1600-2000 | 1100-1500 | 700-1000 |
 | 2000-3000 | 2000-2600 | 1300-2200 | 1000-2000 | 700-1600 | 500-1100 | 400-700 |
 | - | - | 400-1300 | 100-1000 | 0-700 | 0-500 | 0-400 |
 | 500-2000 | 500-2000 | 500-2000 | 500-2000 | - | - | - |
 | 0-500 | 0-500 | 0-500 | 0-500 | 0-500 | (0-500) | (0-500) |
HARDINESS
| Symbol | Meaning |
| The plant tolerates low temperatures (-10º C down to -15º C), it can be covered by snow for months (1 - 8 months). | |
|
| The plant tolerates low temperatures (-5º C), can tolerate occasional snow cover for up to a couple of weeks per year. |
| The plant does not tolerate snow, but can tolerate occasional freezing spells of about - 3º C (the typical morning frost of central Chile in winter) | |
| The plant does not tolerate freezing. |
* Note: The resistance to snow and frost for annual plants indicates that they can achieve their growth and fruiting within the warm season of the area which is defined by the hardiness conditions. It does not mean that the plant in growth can actually endure the conditions associated with the hardiness symbol.
LIGHT EXPOSURE
Similar to the altitude, this variable is not absolute, but relative. It indicates the light conditions which correspond to the habitat where this plant can be found.
| Symbol | Meaning |
| Exposed, but with protection from direct sun through coastal fog. | |
| Deep ravines facing south with additional shadow from trees. Or with a very dense vegetation cover which gives 80 - 90 % shadow (for instance, the Valdivian forests) | |
|
| Steep slopes facing south. Or with a vegetation cover which filters 40 - 80 % of light. |
| Some protection against the sun, some shadow from vegetation, filtering about 20 - 40 % of light. | |
| Fully exposed to sun. Level areas or slopes facing north. |
SOIL HUMIDITY AND WATERING
| Symbol | Humidity |
| Coastal fog/camanchaca: The plants obtain water mainly from condensation. | |
|
| Extremely dry areas with very rare rainfall. The dry season lasts 8 - 12 months and in some years almost no rainfall is possible. Average rainfall is less than 100 mm/year. |
| Dry, arid areas, with long draught periods of 6 - 10 months. Precipitations of 100 mm - 300 mm. are concentrated in winter. | |
| Somewhat dry areas where the draught may last 4 - 5 months. Precipitations of 400 - 800 mm, concentrated in winter. | |
| Humid areas, with almost constant rainfall. Short dry periods are possible (generally not longer than 1 month). | |
|
| The plant grows in water or it has its roots within a permanent water course. This corresponds to marshes, bogs, water courses, lake and river shores. |
LIFE FORM
| Symbol | Meaning |
|
| Tree. |
| Shrub. | |
| Perennial plant. | |
| Annual plant. | |
|
| Biannual plant. |
|
| Climber. |
|
| Climber. |
| Bulb plant. |
FLOWER: COLOR AND NUMBER OF PETALS
These icons define the color and number of petals. Strictly speaking the petals may refer to
| Means a flower of 5 yellow petals. |
| Icon | Description |
| 2 Lobules | |
| 3 Petals. | |
|
| 4 Petals. |
| 5 Petals. | |
| 6 Petals. | |
|
| 7 - 15 Petals. |
| 15- 100 Petals and also asteraceae (This may be frowned upon from the scientific point of view, but is very practical). | |
| Unknown number of petals, without information |
| Icon | Description |
| White, including those flowers with white-yellowish or light blue or light pink tinge. Greenish color is excluded. | |
| Yellow. Greenish color is excluded. | |
| Blue, Dark blue, violet, and almost black. | |
| Red, brown, orange (excluding almost black flowers). | |
| Green. Includes yellow-green and white-green. | |
|
| Color unknown or without information. |
GERMINATION
Germination percentage of the seeds
| Low germination, less than 30 % | |
|
| Average germination, 30 % - 60 % |
| Good germination, 60 - 80 % | |
| Almost complete germination, over 80 % |
SEEDS / KG
Number of seeds per kg. For the calculation the seeds in their optimum condition for storage are taken (usually dry, unless they may not be dried out).